一、示例说明
程序输入为种子用户ID数据集合,每一行包括用户ID和256维用户特征,用户特征数据类型为浮点型数据(存在部分数据用科学计数法表示的情况,比如1.4283673760891302E-4),所有数据分隔符为逗号,ID处于第1个位置,其它256维特征按照顺序处于2-257个位置。其中1-128维为连续性特征,数据都大于等于0小于等于1,余下129-256维为分类型特征经过one-hot处理过后的稀疏数据,数据都为0或者1。如下格式: ID0001,0.1,0,0.56,…,0,1
保存变量的结构体如下:
typedef struct User{
string id;
float fv[128];
int iv[128];
};
计划读取文件每一行记录一个User变量的成员,元素1为id,元素2~129为fv,元素130~257为iv
二、读取文件代码
示例代码:
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct {
string id;
float fv[128];
int iv[128];
}User;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
fstream seedf("C:\\Users\\linxuesong\\Desktop\\cpp\\input\\seed.txt");
vector<User> users;
while(!seedf.eof()) {
string oneline;
getline(seedf, oneline);
User user;
// 将一行按逗号分隔
stringstream ss(oneline);
getline(ss, user.id, ','); //先读取一个
string para;
int count = 0; // 用来计数,当读取128个float后就是int了
while(getline(ss, para, ',')){ // 读取剩下的256个
if(count <= 127){
user.fv[count] = stof(para);
}else {
user.iv[count-128] = stoi(para);
}
count++;
}
users.push_back(user);
}
seedf.clear();
seedf.close();
return a.exec();
}
三、涉及到的知识总结
1.fstream
作用:主要用于读写文件
定义:fstream f;
类继承关系如图:
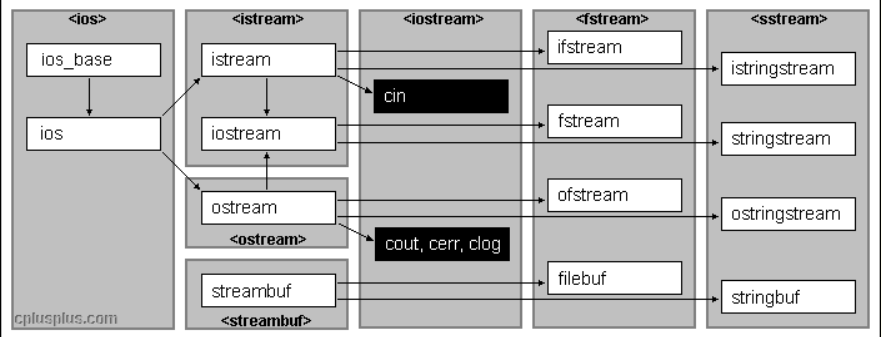
主要方法:
| 函数名 | 参数 | 返回值 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| open | ( const char * filename, os_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in | ios_base::out )// 文件路径和打开方式,打开方式可以省略 | 无 | 以指定的方式打开文件 |
| close | 无参数 | 无 | 关闭文件 |
| bad() | bool | 状态标识符,读写出错 | |
| fail() | bool | 状态标识符,格式错误或读写错误 | |
| eof() | bool | 文件到达结尾返回ture | |
| good() | bool | 没有出现任何错误 | |
| tellg()和tellp()* | pos_type就是一个int | 返回当前读出流\写入流的get、put指针位置 | |
| seekg()和seekp()* | 重载一:pos_type重载二:(off_type offset, seekdir direction) | pos_type就是一个int | 设置读出流\写入流的get、put指针位置 |
简单示例:
vector<string> arrs;
string tmp;
fstream myfile("文件路径"); // 构造函数会调用open方法
if(!myfile) { // fstream重载了!感叹号操作符,fstream对象会返回true或fasle,也可以用!file.good()判断
cout << "文件打开失败";
}
while(!myfile.eof()) { // 直到遇到文件结束符
getline(myfile, tmp); // 取一行
arrs.push_back(tmp);
}
myfile.close();
2.getline
作用: 读取输入流到内存中知道遇到指定的分隔符,默认分隔符为'\n’所以默认时读取一整行
函数原型
/**
*pram1 输入流
*pram2 接收流的内存变量地址
*pram3 分隔符\n,会读取输入流知道遇到分割符,遇到分割符之后停止读取并把分隔符跳过
*/
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim = '\n');
简单示例
四、多线程读取大文件实现(仍旧为完善) 此方法因为文件流的偏移量为int,所以最多可以偏移4G的文件
思路:大文件分隔若干份(cpu有几个核)文件块,对于每一部分以start和end作为标志 seekg设置不同的读取起始位置,每个文件从不同的起始位置读,读到end
需要注意的是我们在读取变量时start可能不是正好的位置,需要对其进行处理,这里是先读取完本行到行末,得到一行结束位置
代码如下
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;
typedef struct {
string id;
float fv[128];
int iv[128];
}User;
typedef struct {
int start;
int end;
}FileBlock;
static vector<vector<User>> aa;
mutex aa_lock;
//获取文件大小 文件偏移量为int, 可以标识2的32次个字节 相当于4G
int getFileSize(string filepath){
fstream f(filepath);
if(!f) {
cout << "打开文件失败" << endl;
}
f.seekg(0, ios::end);
return f.tellg();
f.close();
}
// 获取当前cpu的核数 / 线程处理参数为 param1文件地址 parm2读取文件的位置 param3
int getCpuCoreCnt() {
return thread::hardware_concurrency();
}
// 将文件分为cpu核心个部分,并放入到vector<FileBlock>中
vector<FileBlock> splitFile(string filepath) {
vector<FileBlock> fileBlocks;
fstream f(filepath);
if(!f) {
cout << "打开文件失败" << endl;
}
int fsize = getFileSize(filepath);
int cpu_core_cnt = getCpuCoreCnt();
int block_size = ceil(fsize/cpu_core_cnt); //向上取整,为了防止向下取整导致最后涵盖所有
int start=0,end;
for(int i = 0; i < cpu_core_cnt; i++) {
end = (i+1)*block_size; // 当访问最后一个访问块时可能会超出范围
if(end >= fsize) {
end = fsize;
fileBlocks.push_back(FileBlock{start, end});//已经是最后一行了就结束吧
break;
}
{ // end可能不正好在文件的一行的结尾\n处,去下一行
f.seekg(end);
string tmp;
getline(f, tmp);
}
end = (long)f.tellg()-1;
fileBlocks.push_back(FileBlock{start, end});
start = f.tellg();
}
return fileBlocks;
}
// 之后各个线程按文件的起始位置进行读取
void thread_read_file(FileBlock fb, string filepath) {
fstream seedf(filepath);
vector<User> users;
seedf.seekg(fb.start);
while(seedf.tellg()<=fb.end && !seedf.eof()) {
string oneline;
getline(seedf, oneline);
User user;
// 将一行按逗号分隔
stringstream ss(oneline);
getline(ss, user.id, ','); //先读取一个
string para;
int count = 0; // 用来计数,当读取128个float后就是int了
while(getline(ss, para, ',')){ // 读取剩下的256个
if(count <= 127){
user.fv[count] = stof(para);
}else {
user.iv[count-128] = stoi(para);
}
count++;
}
users.push_back(user);
}
lock_guard<mutex> lock(aa_lock);
aa.push_back(users);
seedf.clear();
seedf.close();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
string filepath ="C:\\Users\\linxuesong\\Desktop\\cpp\\input\\seed.txt";
vector<FileBlock> fbs = splitFile(filepath);
for(int i = 0; i<getCpuCoreCnt(); i++) {
thread t(thread_read_file, fbs[i], filepath);
t.join();
}
this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
cout << aa.size()<<endl;
for (int i =0;i<(int)aa.size();i++)
for(int j; j<(int)aa[i].size();j++)
cout << aa[i][j].id << endl;
return 0;
}





